Digestive health and lactose
Digestive health is an increasingly important issue for consumers. In fact, since the Covid pandemic interest in this subject has never stopped growing. Particular Attention is being paid to numerous ingredients and foods that can be a source of digestive discomfort. Lactose intolerance is one of the aspects that particularly concern consumers. In the face of this trend the food industry seeks to meet consumer expectations by offering new lactose-free products.
Why is digestive health so important ?
Digestion is carried out by our digestive system, which consists of the digestive tract, the pancreas, the liver and the gallbladder. It is essential for it to function properly as it is responsible for the absorption of the micro and macro-nutrients contained in food.[1] Food is transformed along the full length of the digestive system, through various mechanical and chemical stages that involve saliva, chewing, bile acids and enzymes. [1,2]
Digestion may at times be disturbed by various factors. These are sometimes associated with certain foods that are difficult to assimilate but the problem may also result from a dysfunction of the digestive system and lead to diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease or even lactose intolerance. These failures of the digestive system are manifested by abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, gas, nausea, and sometimes weight loss.[3] It is therefore important to be attentive to digestive health and be able to adapt one’s diet accordingly.

Lactose intolerance is the result of an inability to digest the sugar contained in milk and its by-products. A large number of people exclude dairy products from their diet because of it. However, it is important to consume them as they provide numerous nutrients such as calcium and vitamins. Cutting out dairy products altogether can lead to health problems, in particular bone problems, high blood pressure and a high risk of developing diabetes.[8] To deal with this problem, which affects a large proportion of the global population, lactose-free dairy ingredients have been developed, thus making it possible to develop lactose-free food products.
To find out more about lactose intolerance, Lactalis Ingredients recommends the following article: The lactose-free market: what are the opportunities for lactose-free dairy ingredients ?
Lactose-free dairy products, a very contemporary trend
The market for lactose-free dairy products is attracting more and more customers. “In France, 20 % to 50 % of adults do not fully digest lactose”. [4] At global level, this figure rises to 68 %.[5] A study conducted in 2020 reports that 26 % of consumers who buy milk are interested in claims that mention a digestive health boost.[12] In China, 50 % of milk consumers believe that lactose is responsible for digestive discomfort, including bloating and diarrhea.
The market for lactose-free dairy products is growing. It was valued at 13.5 billion USD in 2022 and estimated at 23.1 billion USD in 2032. It can be divided into several categories: milk, cheeses, ice creams, desserts and yogurts. These products are experiencing strong growth due to intolerances and allergies.[6]
North America represents the largest share of the market for lactose-free products, with the United States at the forefront. In Europe, Germany is the main consumer. In East Asia, China accounts for the largest market share.[6] The consumption of lactose-free products is expected to increase in Asia and Latin America over the coming years. Populations in these regions have a high prevalence of lactose intolerance and are becoming more aware of the condition.[11]
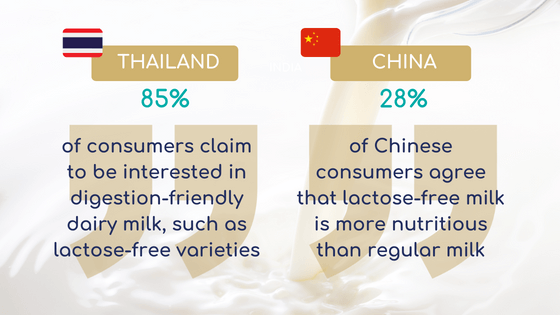
Figure 1 : Why consumers are interested in lactose-free products [13]
Products either without lactose or with a low lactose content represent 38 % of dairy products, followed by desserts and ice cream at 20 %, pastries at 12 % and chocolate at 8 %. Other applications are also possible such as, for example, sports drinks and ready meals.[7]
Lactose-free milk powders from Lactalis Ingredients
Lactalis Ingredients offers a broad range of milk powders. To meet the growing demand for products without lactose, we offer lactose-free / low-lactose skimmed milk power.
-
-
- Lactose-free skimmed milk powder has less than 0.1 g of lactose per 100 g of powder
-
-
-
- Low-lactose skimmed milk powder has less than 1.5 % lactose
-
Lactose-free milk powder is produced by means of enzymatic hydrolysis of the lactose. This produces glucose and galactose. The resulting milk powder is sweeter and more easily assimilated by the body than a standard milk powder.

There are numerous possible applications in dairy products, ice creams and chocolate.
The hydrolysis of lactose (disaccharide) produces monosaccharides, which are sweeter. This therefore allows a reduction of the sucrose content in derived dairy products such as yogurts and flavored milks, and a reduction of up to 25 % in ice cream. Moreover, this reduction reduces the risk of a sandy texture and therefore increases the palatability of the ice cream. [9,10]
The use of lactose-free milk powders in ice cream also makes it possible to achieve a product with a more supple texture. This is because the glucose and galactose obtained through the lactose hydrolysis lower the ice crystallization point. So at the same temperature, a lactose-free ice cream will be softer than an ice cream containing lactose.
Lactose can also be the cause of a grainy texture in ice cream due to its crystallization. The hydrolysis process helps prevent this phenomenon and thus creates a pleasanter texture. Moreover, the use of lactose-free milk powders in ice cream does not affect the acidity and density of the final product.[10]
Chocolate goods can also be included in the “lactose-free” market. Lactose-free chocolates can be produced simply by replacing the standard milk powder with a lactose-free powder. Consumers can thus enjoy both indulgence and digestive well-being.
Sources :
[1] National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Your Digestive System & How it Works, 2017
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/digestive-system-how-it-works
[2] Vidal, Comment digérons-nous les aliments ?, 2019 https://www.vidal.fr/sante/nutrition/corps-aliments/digestion-aliments.html
[3] National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Digestive Diseases,
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases
[4] Ameli, Intolérance au lactose : définition et symptômes, 2021,
https://www.ameli.fr/assure/sante/themes/intolerance-lactose/definition-symptomes
[5] ] Christian Løvold Storhaug , Svein Kjetil Fosse , Lars T Fadnes, Country, regional, and global estimates for lactose malabsorption in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis, 2017 Oct,
DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30154-1
[6] Future market insights reports, FMI, Lactose Free Dairy Products Market Outlook (2022-2032), July 2022, https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/lactose-free-dairy-products-market
[7] Mintel, GNPD
[8] Peter J. T. Dekker, Damiet Koenders, and Maaike J. Bruins, Lactose-Free Dairy Products: Market Developments, Production, Nutrition and Health Benefits, 2019, doi: 10.3390/nu11030551
[9] Peter J. T. Dekker, Damiet Koenders, and Maaike J. Bruins, Lactose-Free Dairy Products: Market Developments, Production, Nutrition and Health Benefits, 2019, doi: 10.3390/nu11030551
[10] Soleiman Abbasi, Arman Saeedabadian, Influences of lactose hydrolysis of milk and sugar reduction on some physical properties of ice cream, 2013, Journal of Food Science and Technology
[11] Future market insights reports, FMI, Lactose-free Products Market Outlook (2022-2032), oct 2022, https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/lactose-free-products-market
[12] Ophélie Buchet, What is next for lactose-free milks?, Mintel, 2021
[13] Michelle Teodoro, Nutrition watch: lactose-free dairy in APAC, Mintel, 2021